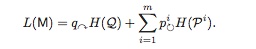Overlapping Community Detection
Overlapping Community Detection in Networks : the State of the Art and Comparative Study
0 OLD METHOD
-
Clustering
-
Graph Cut
-
Modularity-Based Method(is NP-hard to optimize) [Newman, 2006]
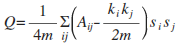
-
Greedy
-
Simulated Annealing
-
-
Girvan-Newman Algorithm (Betweenness, split)
-
Spectral Method
1 Clique Percolation
CPM (Clique Percolation Method)
-
Indentify all the k-cliques in network. Clique is an intensively structure, each two nodes are connected in a clique. Connect two nodes if their two k-cliques they belong to share k-1 members. [Palla, 2005, Nature]
-
Implementation: CFinder (support directed and weighted graph)
-
Time Complexity: polynomial (NP-complete maximal cliques finding)
2 Local Expansion and Optimization
LFM
-
expands a community from a random seed node to form a natural community until fitness function is locally maximal. [Lancichinetti, 2009, New J. Phys.]
-
fitness function:
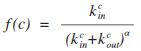
-
where nc is the number of communities, s is the average size of communities.
-
O(ncs2), computation complexity is depended on parameter \alpha.
-
worst-case complexity: O(n2)
GCE (Greedy Clique Expansion)
-
takes all maximum cliques as initial seeds to greedily expand the fitness function to find overlapping communities. [Lee, 2010]
-
Greedy expansion complexity: **O( E M)** , M is the number of cliques to be expanded. -
merge complexity: **O(2( C1 + C2 )-1)** (not sure)
OSLOM (Order Statistics Local Optimization Method)(IMPORTANT)
- optimizes locally the statistical significance information of a cluster with respect to random fluctuation with Extreme and Order Statistics. It tests the statistical significance of a cluster with respect to a global null model. It can deal with weighted, directed edges, overlapping communities, hierarchies and dynamic communities. [Lancichinetti, 2011]
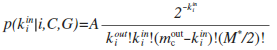
-
Implementation: www.oslom.org
-
worst-case complexity: O(n2)
EAGLE
-
All maximal cliques is as initial communities, merged by maximum similarity -> dendrogram. The optimal cut on the dendrogram is determined by the extended modularity with a weight based on the number of overlapping memberships. [Shen, 2008] [code]
-
Extended Modularity:
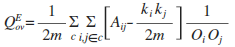
-
where Oi is the number of communities to which node i belongs.
-
O(n2+(h+n)s), where s is the number of maximal cliques, h is the number of pairs of maximal cliques which are neighbors.
3 Mixturl Model (TODO)
- [Newman, 2007]
- GMM(Gaussian Mixture Model)
- SBM(Stochastic block model)
- NMF(Non-negativeMatrix Factorization)
4 Label Propagation Algorithm (Dynamical Algorithm)
COPRA
-
O(vmlog(vm/n)) per iteration, v controls the number of communities a node can belong to, m is the number of edges, n is the number of nodes.
SLPA(IMPORTANT TODO)
-
is a general speaker-listener based information propagation process. [Xie, 2011]
-
**O(t E )**, linear, t is the predefined maximum number of iterations.
InfoMAP(IMPORTANT TODO)
- The map equation framework